Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-19 Origin: Site








You live in a space area called the solar system. The sun is at the center of this system. There are eight planets in the solar system. There are also 18 dwarf planets and 294 moons. Scientists have found over a million asteroids. They have also found almost 4,000 comets.
| Category | Officially Recognized Count |
|---|---|
| Planets | 8 |
| Dwarf Planets | 18 |
| Moons | 294 |
| Asteroids | Over 1,000,000 discovered |
| Comets | Nearly 4,000 discovered |
The sun has almost all the mass in the solar system. Its gravity keeps everything together. Learning about this helps you see how science changes. The sun’s energy helps solar cells make clean power for us.
The solar system has eight planets. It also has many dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. The Sun’s strong gravity holds everything together.
The Sun has almost all the mass in the solar system. It gives energy that helps life on Earth. It also powers solar technology on Earth.
Planets are split into two groups. There are small, rocky inner planets. There are also large gas or ice outer planets. Each planet is different and has its own distance from the Sun.
Dwarf planets go around the Sun but do not clear their paths. Moons go around planets. Some moons are bigger than some planets.
New discoveries show the solar system still has surprises. Better solar technology helps us use the Sun’s energy more easily.

You live in a galaxy called the Milky Way. The solar system is your home within this galaxy. It sits about 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way. You can find it on the inner edge of a minor spiral arm named the Orion Arm. This arm lies between two larger arms, the Perseus Arm and the Scutum-Centaurus Arm. The Orion Arm is a quiet place, which helps protect planets like Earth from strong radiation. Many bright stars and interesting objects surround the solar system, making the night sky beautiful and full of wonders.
Did you know? The solar system’s location in the Orion Arm helps keep life on Earth safe from dangerous cosmic events.
The solar system has a clear structure. At the center, you find the Sun. The Sun holds almost all the mass in the solar system and keeps all the bodies orbiting around it with its gravity. Moving outward from the Sun, you first see the four terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These planets have rocky surfaces and metal cores.
Next, you reach the asteroid belt. This region sits between Mars and Jupiter. It contains many rocky objects, including the dwarf planet Ceres. Beyond the asteroid belt, you find the gas giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are much larger and made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
Farther out, you discover the dwarf planets and icy comets. Dwarf planets like Pluto and Eris orbit the Sun but do not clear their paths of other objects. Comets come from the Kuiper Belt and the distant Oort Cloud. Their orbits are long and stretched out, sometimes bringing them close to the Sun and then far away again.
The solar system’s main parts, in order from the Sun:
The Sun
Terrestrial planets
Asteroid belt
Gas giants
Dwarf planets and comets
Each part follows its own path, but all stay connected by the Sun’s gravity.

The solar system has many interesting parts. You can learn about each one to see how they fit together. The main components are the sun, eight planets, five big dwarf planets, hundreds of moons, and millions of asteroids and comets. Each part has its own job in making the solar system an active place.
The sun is in the middle of the solar system. It has almost all the mass—about 333,400 times more than Earth. Its gravity keeps planets, satellites, and other things moving around it. The sun is a huge ball of hot, glowing gas. It is made mostly of hydrogen and helium. There is no solid surface on the sun. It has layers like the core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. The core is where nuclear fusion happens. This makes the energy that lights and heats the solar system.
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter | About 1.39 million km (109 times Earth) |
| Mass | 1.99 × 10⊃3;⁰ kg (333,400 Earth masses) |
| Mean density | 1.41 g/cm³ |
| Surface gravity | 273 m/s⊃2; (27.9 times Earth's gravity) |
| Effective temperature | 5800 K |
| Luminosity | 3.8 × 10⊃2;⁶ watts |
| Rotation period at equator | 24 days 16 hours |
The sun gives energy that is needed for life on Earth. You use this energy with solar cells. Solar cells change sunlight into electricity. This technology helps power homes, schools, and some vehicles with clean energy.
The sun’s gravity works like a giant anchor. It holds all the main parts of the solar system in place.
There are eight planets in the solar system. Each planet goes around the sun and has special features. The planets are in two groups: terrestrial (rocky) and giant (gas or ice).
| Planet | Order from Sun | Key Features | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 1st | Smallest planet, closest to the Sun | Inner terrestrial planet |
| Venus | 2nd | Sixth largest planet | Inner terrestrial planet |
| Earth | 3rd | Our home planet, fifth largest | Inner terrestrial planet |
| Mars | 4th | Seventh largest planet | Inner terrestrial planet |
| Jupiter | 5th | Largest planet, gas giant | Outer gas giant |
| Saturn | 6th | Second largest planet, gas giant | Outer gas giant |
| Uranus | 7th | Third largest planet, ice giant | Outer ice giant |
| Neptune | 8th | Fourth largest planet, most distant | Outer ice giant |
The inner planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars—are small and rocky. The outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are much bigger. Jupiter is the largest planet. Mercury is the smallest. The space between the planets gets bigger as you move away from the sun.
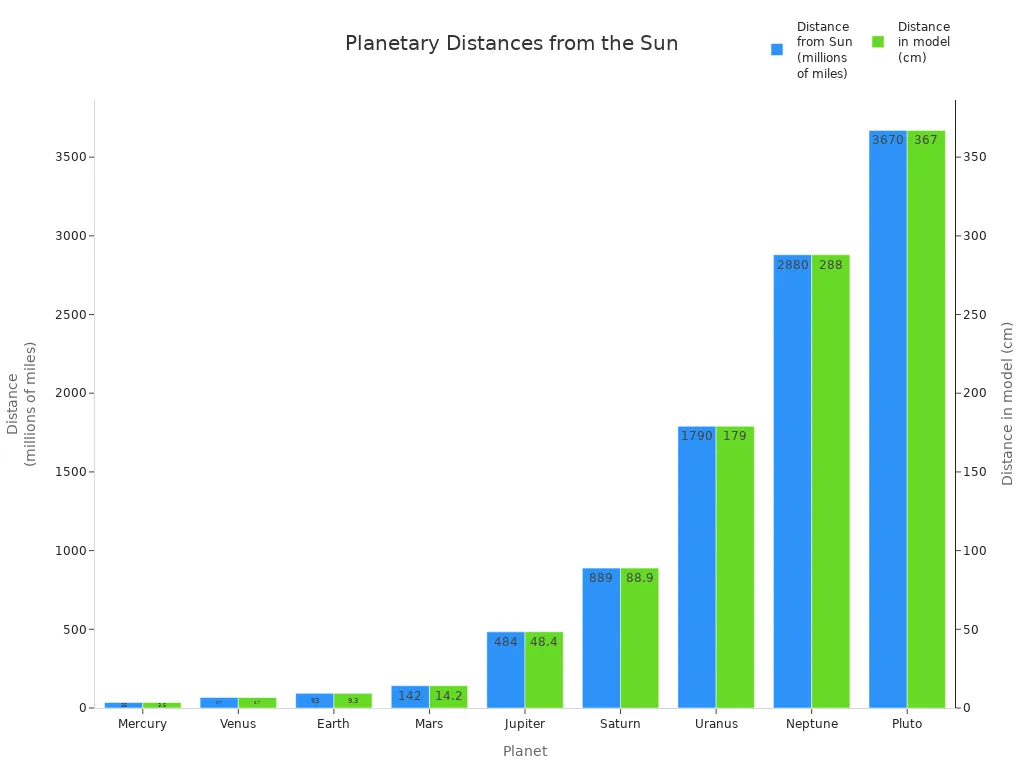
You can see the planets are not spaced evenly. The inner planets are close together. The outer planets are far apart. This big difference in size and distance makes the solar system fun to study.
Dwarf planets are another key part of the solar system. They go around the sun and are almost round. But they do not clear their paths of other objects. The five most well-known dwarf planets are Ceres, Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris.
Ceres: It is in the asteroid belt. It is the smallest dwarf planet and has shiny salt spots.
Pluto: It used to be called the ninth planet. It has an icy surface and five moons.
Haumea: It is shaped like an egg and spins fast. It has two moons and a ring.
Makemake: It has a bright, reddish surface and one moon.
Eris: It is almost as big as Pluto. It is the heaviest dwarf planet and has one moon.
Dwarf planets help you learn about the history and variety of the solar system.
Moons, also called natural satellites, go around planets and dwarf planets. In 2025, there are over 891 confirmed moons in the solar system. Jupiter has the most moons, with 95. Saturn is next with 274. Some moons are bigger than planets. For example, Ganymede, a moon of Jupiter, is larger than Mercury.
| Planet | Confirmed Number of Moons |
|---|---|
| Mercury | 0 |
| Venus | 0 |
| Earth | 1 |
| Mars | 2 |
| Jupiter | 95 |
| Saturn | 274 |
| Uranus | 28 |
| Neptune | 16 |
Some moons, like Europa and Titan, have features that interest scientists. Europa might have an ocean under its ice. Titan has a thick atmosphere.
Asteroids and comets are small but important in the solar system. There are about 1.4 million asteroids. Most are in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids are rocky and come in many shapes and sizes. Some are only a few meters wide. Others are hundreds of kilometers across.
Comets are icy and travel in long paths around the sun. When a comet gets close to the sun, its ice turns into gas and dust. This makes a glowing tail. There are about 4,000 known comets in the solar system. Most comets come from the Kuiper Belt or the faraway Oort Cloud.
Asteroids are rocky and stay mostly in the asteroid belt. Comets are icy and make bright tails when they get near the sun.
These main parts of the solar system work together. They make a complex and beautiful space neighborhood. By learning about them, you find out more about your place in the universe.
Almost all the mass in the solar system is in one place. The Sun holds about 99.85% of the total mass. This means the Sun is much heavier than everything else. The eight planets together have only about 0.135% of the mass. All the smaller bodies, like moons, asteroids, comets, and dwarf planets, add up to just 0.015%.
| Mass Component | Approximate Percentage of Solar System Mass |
|---|---|
| Sun | About 99.85% |
| Eight Classical Planets | About 0.135% |
| Smaller Bodies (moons, comets, Kuiper belt objects, dwarf planets, asteroids, meteoroids, interplanetary medium) | About 0.015% |
Dwarf planets have masses close to big moons. For example, the Moon’s mass is about 7.342 × 10⊃2;⊃2; kg. Dwarf planets are round but not as heavy as planets. Planets are much heavier, with masses above 10⊃2;⁴ kg. Most of the solar system’s weight comes from the Sun. Planets and smaller objects make up only a tiny part.
The Sun’s huge mass makes strong gravity. This gravity keeps planets and other bodies moving around it.
The solar system has many kinds of objects. Each type has special features and a job in the system.
| Celestial Body Type | Description | Examples | Categorization Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stars | Massive, luminous spheres of plasma held by gravity, producing energy via nuclear fusion | Sun | Energy generation, composition (plasma), luminosity |
| Planets | Large bodies orbiting a star, having cleared their orbital paths | Earth, Mars, Jupiter | Orbit clearing, size, composition (rocky or gaseous) |
| Dwarf Planets | Similar to planets but have not cleared their orbits | Pluto, Eris, Haumea | Orbit not cleared, size |
| Moons | Natural satellites orbiting planets or dwarf planets | Earth's Moon, Europa | Orbiting another body, size varies |
| Asteroids | Small, rocky objects orbiting the Sun, mostly in asteroid belt | Ceres, Vesta | Size, composition (rocky), orbit location |
| Comets | Icy bodies releasing gas and dust near the Sun, forming tails | Halley's Comet | Composition (icy), behavior near Sun |
| Meteoroids | Small rocky or metallic objects in space | N/A | Size, composition |
You find stars like the Sun that give off light and heat. Planets go around the Sun and can be rocky or gas giants. Dwarf planets also go around the Sun but do not clear their paths. Moons go around planets or dwarf planets. Asteroids are rocky and mostly found in the asteroid belt. Comets are icy and grow tails when near the Sun. Meteoroids are small rocks or metal pieces moving through space.
Learning about the solar system’s parts helps you see how they fit together. This knowledge shows the balance and variety in your cosmic neighborhood.
You live in a time of exciting discoveries in the solar system. Since 2020, astronomers have found a new dwarf planet called 2017 OF201. This object is about 700 kilometers wide and sits far beyond Pluto, in the inner Oort Cloud. Its orbit stretches from 44.5 to over 1,600 times the distance between Earth and the sun. Scientists used data from powerful telescopes to spot it. The discovery of 2017 OF201 shows that the outer solar system holds many secrets. You might hear about more distant objects in the future as new telescopes scan the sky.
Researchers also found a dwarf planet named 2015 RR245. This object orbits in the far reaches of the solar system. These discoveries help you understand that the solar system is bigger and more complex than you might think. Some of these new objects have strange orbits. They challenge old ideas about how planets and dwarf planets formed. Scientists now believe there could be many more hidden worlds waiting to be found.
New dwarf planets like 2017 OF201 and 2015 RR245 show that your solar system is still full of surprises.
Solar technology has made big leaps forward by 2025. You can now use smarter inverters that adjust power in real time and let you check your solar panels with an app. Next-generation batteries, such as lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate, store energy better and help you use solar power even when the sun is not shining. Dynamic monitoring platforms track your system’s performance and spot problems early.
Smarter inverters with real-time adjustments and app-based monitoring.
High-capacity batteries for reliable energy storage.
Dynamic solar monitoring for early issue detection.
Sleek solar roof designs that look good and make energy.
AI-driven systems that learn your habits and save energy.
Microinverters for each panel to boost efficiency.
Resilient features for storm protection.
You also see new solar panels that use advanced materials like perovskite, which can reach about 30% efficiency. Some buildings now have solar cells built right into their windows or roofs. Thin-film panels use less energy to make and cost less than older types. These advances help you use the sun’s energy in more ways and make clean power a bigger part of your life.
The latest solar technology lets you use the sun’s power more efficiently and safely, helping you and the planet.
You have learned about the solar system’s main parts. These include the sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets. Each one helps shape your space neighborhood in a special way. The sun gives energy that supports life. It also helps solar cells make power for new technology.
If you stay curious about new discoveries, you can see how the solar system changes your daily life and inspires you to explore more.
A planet clears its orbit of other objects. A dwarf planet does not. Both go around the Sun and have enough gravity to be round. Pluto is a famous dwarf planet.
Solar cells take sunlight and turn it into electricity. You can use this power for homes, schools, and devices. Solar cells help you use clean energy every day.
Big planets like Jupiter and Saturn have strong gravity. They can catch more moons. Small planets like Mercury and Venus have weak gravity. They do not have any moons.
Most asteroids stay in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Comets come from the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. These places are far from the Sun.
Yes! You can see planets like Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn with your eyes. The Moon is easy to spot. Try looking up at night for these bright objects.
